- Classical Conditioning: Ivan Pavlov, John B Watson

image from: http://www.fadooda.com/index.php?itemid=156

- Discovered by accident by Ivan Pavlov, in his experiment with his dog, he noticed that dog salivated when it saw a person brought its food before the food was given
- John B Watson focused on stimulus and response
Terms in Classical Conditioning
Neutral Stimulus (NS): external stimulus that does not ordinarily cause a reflex response
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): a stimulus that evokes an unconditional response before conditioning
Unconditioned Response (UCR): an under reaction to unconditioned stimulus before previous conditioning
Conditioned Stimulus (CS): previously neutral then has true conditioning acquire ability to evoke a condition response
Conditioned Response (CR): learn reaction to a condition stimulus that occurs because of previous conditioning
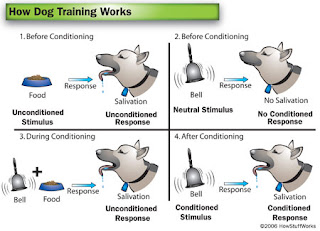
Example:
Before Conditioning
Bell -> no relevant response (means: no salivation)
Meat -> salivation
During Conditioning
Bell + Meat -> Salivation
After Conditioning
Bell -> Salivation
reference: Course Manual (Learning in Young Children, Najihah Akeb-Urai, International Islamic
College)
- Operant Conditioning: B. F. Skinner

- Reinforcement: refers to any action that increase the probability of response or behavior
- Positive reinforcement: increasing of the rate of response when a stimulus is presented
example -> verbal praise, a token (such as sticker)

image from: http://chips.org.au/body.htm
- Negative reinforcement: increasing the rate of response when a stimulus
example -> Amir is told to leave the class when he make noise
example -> Amir is told to leave the class when he make noise

- Punishment: decreasing the rate of response when a stimulus is presented


 Posted by
Posted by